- •Failure of Carrefour internationalization strategy in Russia
- •Contents
- •Introduction 3
- •1. 1. Company Overview 4
- •Introduction
- •Chapter 1. Background
- •1. 1. Company Overview
- •1. 2. History of the company Carrefour: hypermarket pioneer.
- •1.3 . Internationalization
- •1.4 . Russian Retail Sector
- •Chapter 2. Theory and Problem
- •Chapter 3. Methodology
- •3. 1. Pest-analysis Political factors (including institutions and infrastructure)
- •Economic factors
- •Technological
- •Retail Trade in Russia
- •3. 2. Swot-analysis
- •Increasing awareness of customers with European Brands
- •Chapter 4. Company figures
- •Chapter 5. Recommendations
Chapter 3. Methodology
3. 1. Pest-analysis Political factors (including institutions and infrastructure)
Administrative barriers and infrastructure barriers have a great effect on the retail market in Russia.
The below stated administrative barriers are marked for having a negative effect on the market:
• Bureaucracy, which implies excessive amounts of paperwork and obstacles in importing goods and obtaining space.
• Regional differentiation of public administration: Regional authorities are able to establish different rules and recommendations that result in additional barriers which force retailers to develop different policies in different regions. Participants point out that one of the most widespread barriers for fast regional development is the recommendation to purchase from local producers, who are often not able to provide products of sufficient quality regularly. This system conflicts with the logistic system established by retailers and reduces cost effectiveness.
Infrastructure barriers are following:
• Lack of retail space and rising prices for retail space in large cities. This is especially critical in Moscow, where the retail space market is considered saturated. All large retailers have special departments to cope with these issues;
• Lack of warehouse facilities: This is a common issue faced by retailers in all of Russia’s largest regions. Many overcome this problem by constructing their own distribution centers;
• Limited transportation infrastructure: Retailers face the problem of deliveries delay and longer transit periods due to poor roads and heavy traffic. The situation is forecast to worsen in the next two to three years;
• Lack of electricity and poor lines of communications in the regions: Retailers complain of a lack of energy in some regions, and lack of proper communication channels for existing facilities.
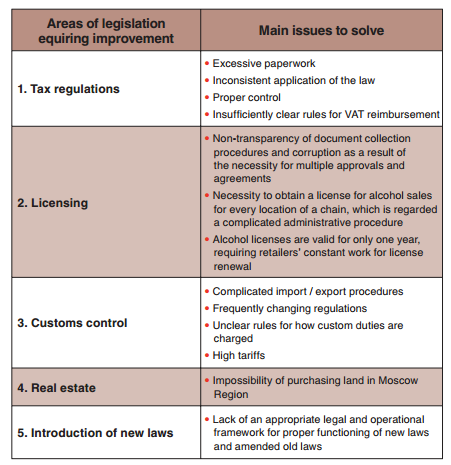
Most participants complain about the corruption, complexity of legislation, bureaucratic procedures, unclear wording of laws and excessive paperwork in all areas covered by regulations. There are five main directions for legislation improvement based on retail market player needs:12
Also Russia’s movement towards International Financial Reporting will lead to significant improvements, as they are more complicated and time consuming than international standards.
Economic factors
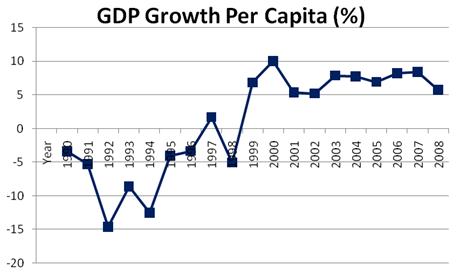
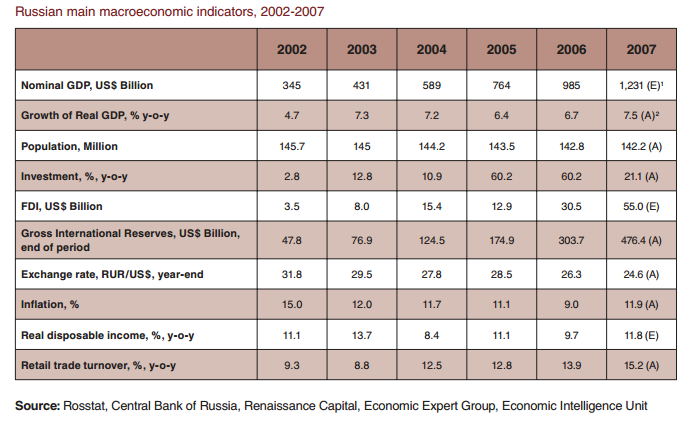
Over the last eight years, Russia has been one of the fastest growing markets in the world. According to official statistics, the GDP increased from US$196 billion in 1999 to around US$1,231 billion in 2007, representing an average annual growth rate of 30% (in nominal dollar terms). The main factors driving the economy include an increase in the price of natural resources, an increasing inflow of capital into the economy, an increase in the population’s income and spending, diversification of the industrial base and a reduction in personal and corporate tax rates. During the last five years, the economy’s growth rate has been increasing; in 2007, GDP increased by 7.5% in real terms. The Russian consumer is one of the main beneficiaries of economic growth, with real disposable income growing faster than the GDP at an average of 11% annually over the last five years.13
|
Source: Rossstat
Carrefour decided to enter the Russian market in the least favorable period. Historically, from 2006 until 2012, Russia Retail Sales YoY averaged 8.4 Percent reaching an all-time high of 17.7 Percent in December of 2007 and a record low of -9.8 Percent in September of 2009.14
Speaking about the Russians’ consumer Spending the situation was also bad at that time. According to the Table 2 we can see the following figures.
T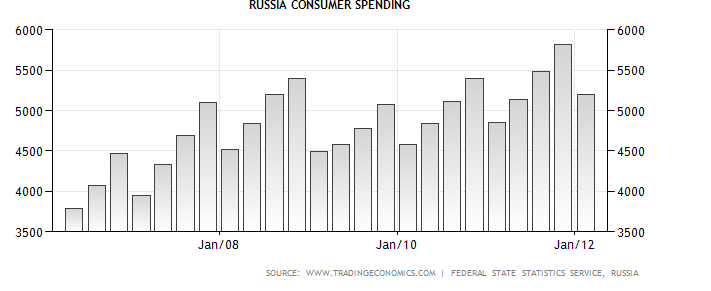 able
2 Russia Consumer Spending.15
able
2 Russia Consumer Spending.15
The recession, which saw the economy contract by 7.9% in 2009, was particularly bad for consumer-dependent sectors such as retail.16 No wonder, the biggest retail companies are trying to enter Russian market as it was forecasted that Russia will become the 4th largest grocery market by 2015.
However we have to take into account, that the total market share of big supermarket players equals only 30,3 % (Table 3). While 69, 7% is still occupied by small stores. We an conclude that the industry is mainly dominated by small markets, etc. Also the individual sellers play a great role in food sector due to the Russian mentality.
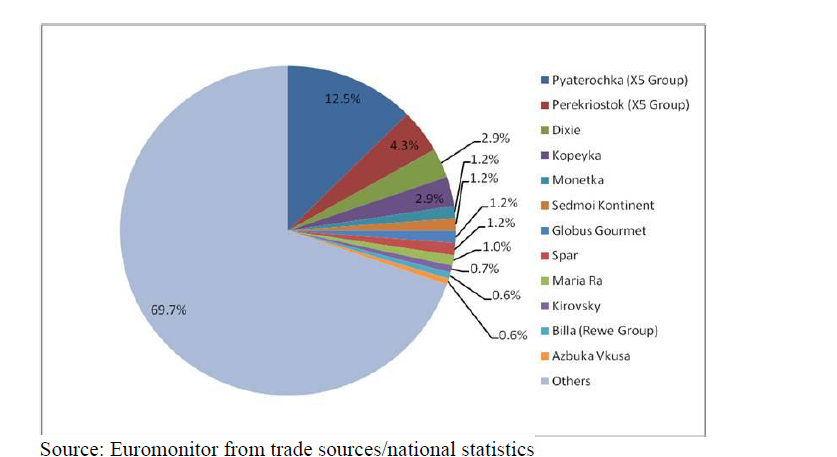
Table 3 Russian Retail Market Share By Company in 2010. Supermarket 17
Social
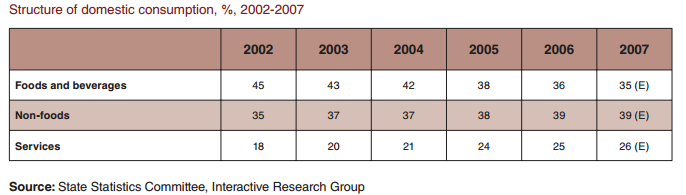
In line with the overall growth of the consumer market, the structure of the Russian consumer basket is changing and moving toward western consumption standards. The share of foods and durable goods is decreasing, while consumer services and non-durable goods are on the rise. The share of non-food purchases in the average consumer basket increased from 35% in 2002 to 39% in 2006, while the share of food and beverages declined accordingly from 45% to 36%.18
Russian markets as well as retail market vary greatly, depending on such factors as popularity of the region, density, urbanization, monthly income and other characteristics. But according to the statistics, the most important for retailers region is , Central Federal Region due to the fact that it occupies the 34,1 per cent in 2010 of Russia’s total sales. 19also there live about 24% of the population. To compare with Far East region, it occupies only 4% of the retail market, although it is the biggest region, considering the amount of territory. What has to be stressed out, is that the largest retailers are focused on Moscow as the main market-focus as it gives the best conditions.
On the one hand, it is a well-known fact that the population decreases constantly. The main focus-group consumers are between 23-45 years old, the other problem of Russia is the ageing of popularity. That leads to the new problems and challenges for companies.
On the other hand, a study by Euromonitor International points out that over 50% of households in Russia moved to the middle class category during the course of the last decade, the fastest growth rate among emerging economies. In fact, between 1998 and 2007, Russia climbed to the 53rd spot in global ranking of wealth from 72nd. Wages also increased commensurate to the economic growth, with disposable income increasing 26% a year.20all that tendency is very important, because it leads to the changes in consumers’ references.
In recent years the world’s tendency of “healthy life” appeared in Russia. That means that people tend to willing pay more for healthy goods, especially in big cities. But in most cases consumers are not aware of the goods’ benefits and do not want to pay more. Nevertheless there is another pattern, it shows that Russian people tend to value foreign products higher, because they are sure that the European quality standards are higher.
Social indicators such as number of passenger cars, mobile phone subscribers and personal computers are also demonstrating improvement and are forecasted to reach the level of other Eastern European countries.

The availability of consumer loans results in increased demand for all types of merchandise.