
матмод (4сем) / 2кр ряды фурье / примеры fourier4
.pdf
Fourier Series vs. Fourier Sine Series vs. Fourier Cosine Series
Find the Fourier series, the Fourier Sine series, and the Fourier Cosine series representations of the following function and sketch the functions to which the three series converges.
0, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1
f (x) =
x, 1 < x < 2
2 |
|
|
f (x) |
|
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
x |
|
|
Fourier Series |
|
|
|||||||
For 0 < x < 2, set |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a0 |
|
∞ |
|
|
nπx |
nπx |
|
||
f (x) = F (x) = |
|
|
|
|
i , |
|||||
2 |
+ n=1 han cos L + bn sin |
L |
||||||||
where |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b − a |
|
2 − 0 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
L = |
= |
= 1. |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Fourier coe cients are calculated as follows.
|
1 |
|
b |
|
1 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
a0 = |
Za |
f (x) dx |
= |
Z0 |
f (x) dx = Z0 |
0 dx + Z1 |
x dx = 0 + |
||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
L |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a0 |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
1 |
Za |
b |
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Z0 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
an = |
f (x) cos |
dx = |
f (x) cos(nπx) dx |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
L |
|
L |
|
1 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
= |
Z0 |
1 |
0 · cos(nπx) dx + Z1 |
2 x · cos(nπx) dx |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
integrate by parts: |
u = x, |
dv = cos(nπx) dx |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
= |
0 + |
|
x sin(nπx) 1 |
− |
|
Z1 |
|
sin(nπx) dx |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
nπ |
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
= |
|
|
[2 sin(2nπ) − sin(nπ)] + |
|
cos(nπx) 1 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
nπ |
n2π2 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
n |
|
||
= |
|
|
[0 − 0] |
[cos(2nπ) − cos(nπ)] = |
− (−1) |
|
since cos(2nπ) = 1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
nπ |
n2π2 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n2π2 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cos(nπ) = (−1)n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
an |
= |
1 − (−1)n |
|
n = 1, 2, . . . |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n2π2 |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
1 |
Za |
b |
(x) sin |
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
Z0 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
bn = |
|
|
f |
|
|
|
dx |
= |
|
|
|
f (x) sin(nπx) dx |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
L |
|
L |
1 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
= |
Z0 |
1 |
0 · sin(nπx) dx + Z1 |
2 x · sin(nπx) dx |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
integrate by parts: u = x, |
dv = sin(nπx) dx |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
= |
0 − |
|
|
x cos(nπx) 1 |
+ |
|
|
Z1 |
|
cos(nπx) dx |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
nπ |
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
= |
− |
|
[2 cos(2nπ) − cos(nπ)] + |
|
sin(nπx) 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
nπ |
n2π2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
− (−1) |
n |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
= |
− |
|
[2 |
− (−1) |
|
] + |
|
|
[sin(2nπ) − sin(nπ)] = |
− |
|
|
|
+ 0 |
|||||||||||||
nπ |
|
n2π2 |
|
nπ |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
bn = − |
2 − (−1)n |
n = 1, 2, . . . |
|
|
|
|
||
|
nπ |
|||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Then,
|
|
|
|
|
a0 |
∞ |
|
nπx |
|
|
nπx |
|
|
||
f (x) = |
F (x) = |
|
+ n=1 han cos |
+ bn sin |
i |
for 0 < x < 2 |
|||||||||
2 |
L |
|
L |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
∞ |
1 |
− (−1)n |
|
|
|
2 − (−1)n |
sin(nπx) |
||||||
= |
+ n=1 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
4 |
n2π2 |
cos(nπx) |
− nπ |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f (x) = |
4 |
+ π n=1 n " |
1 |
nπ |
cos(nπx) − [ 2 − (−1)n ] sin(nπx)# |
0 < x < 2 |
||||
|
3 |
1 |
∞ |
1 |
|
− (−1)n |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
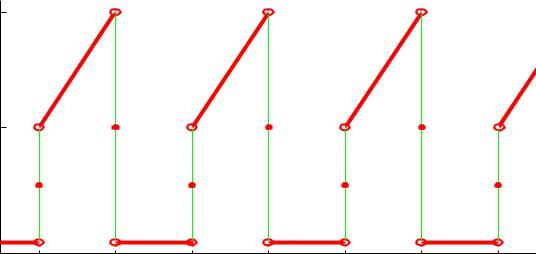
Fourier Series representation of f(x)
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
F(x) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-3 |
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
Fourier Sine Series
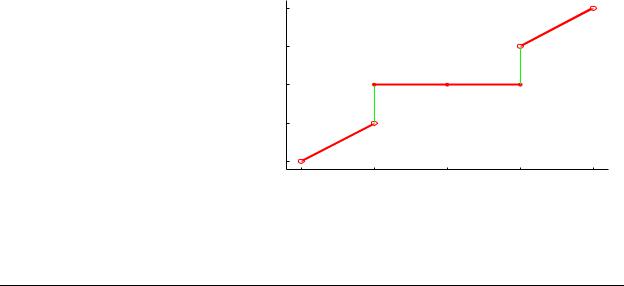
Odd extension of f(x)
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
f0(x) = |
x, |
−2 < x < 1 |
fo(x)1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0, −1 ≤ x ≤ 1 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x, |
1 < x < 2 |
-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
Note that f (x) is defined on the interval [0,2), whereas fo(x) (the odd extension of f (x)) is defined on the interval (-2,2). The Fourier Sine series of f (x) on the interval [0,2) is equivalent to the Fourier series of fo(x) on the interval (-2,2). In this case, we have L = 2 and an = 0 for all n = 0, 1, 2, . . ..
For 0 < x < 2, set
∞ |
nπx |
|
|
|
f (x) = FS (x) = n=1 bn sin |
, |
with L = 2. |
||
L |
||||
X |
|
|
|
The Fourier coe cients are calculated as follows.
bn |
= |
|
L Z0 |
L |
f (x) sin |
L |
dx |
= |
2 |
|
Z0 |
2 |
|
f (x) sin |
|
2 |
|
|
dx |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
= |
Z0 |
1 |
0 · sin |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
x · sin |
|
|
2 |
|
|
dx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
dx + Z1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
nπx |
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
0 − nπ x cos |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
integrate by parts: |
|
|
u = x, |
dv = sin |
|
dx |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
= |
|
2 |
+ nπ Z1 |
cos |
|
2 |
dx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
−nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
+ |
|
n2π2 |
sin |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2 cos(nπ) − cos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
h |
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
= |
− |
|
|
h2(−1) |
− cos |
|
i + |
|
|
hsin(nπ) − sin |
|
|
|
i |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
nπ |
2 |
n2π2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
= |
− |
2 |
h2(−1)n − cos |
nπ |
i + |
|
|
4 |
|
|
h0 − sin |
nπ |
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
nπ |
2 |
n2π2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
bn |
= |
|
|
2 |
|
2(−1)n − cos |
nπ |
|
+ |
|
2 |
|
sin |
nπ |
|
|
|
|
n = 1, 2, . . . |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
nπ |
|
2 |
nπ |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Then,
|
∞ |
nπx |
|
|
|
f (x) = FS (x) = |
n=1 bn sin |
|
for 0 < x < 2 |
||
L |
|||||
|
X |
|
|
|
f (x) = |
|
2 ∞ 1 |
2(−1)n − cos |
nπ |
|
2 |
|
|
nπ |
sin |
|
nπx |
|
0 < x < 2 |
|
−π n=1 n |
2 |
+ nπ sin |
2 |
2 |
|||||||||||
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fourier Sine Series representation of f(x)
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FS (x) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-5 |
-4 |
-3 |
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
Fourier Cosine Series
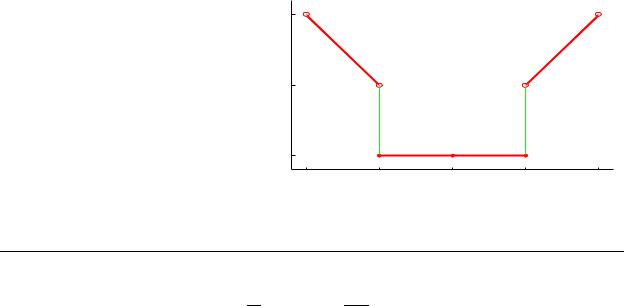
Even extension of f(x)
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
−x, |
−2 < x < 1 |
fe(x) |
|
|
|
|
||
fe(x) = |
0, −1 ≤ x ≤ 1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x, |
1 < x < 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
Note that f (x) is defined on the interval [0,2), whereas fe(x) (the even extension of f (x)) is defined on the |
||||||||
interval (-2,2). The Fourier Cosine series of f (x) on the interval [0,2) is equivalent to the Fourier |
||||||||
series of fe(x) on the interval (-2,2). In this case, we have L = 2 and bn = 0 for all n = 1, 2, . . .. |
|
|||||||
For 0 < x < 2, set |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a0 |
∞ |
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
f (x) = FC (x) = |
+ n=1 an cos |
with L = 2. |
|
|
||
|
|
2 |
L , |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
The Fourier coe cients are calculated as follows.
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
a0 = |
Z0 |
|
f (x) dx |
= |
|
Z0 |
f (x) dx = Z0 |
0 dx + Z1 |
x dx = 0 + |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
L |
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a0 |
|
= |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
an |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
f (x) cos |
L |
|
dx |
|
= |
|
2 |
|
2 |
f (x) cos |
|
2 |
|
dx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
L Z0 |
|
|
|
|
Z0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
= |
|
1 |
0 · cos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
x · cos |
|
|
2 |
|
|
dx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Z0 |
|
2 dx + Z1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
|
|
= cos |
2 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
0 + nπ x sin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
integrate by parts: |
|
u |
|
|
|
x, |
dv |
|
|
|
|
|
dx |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
= |
|
2 |
|
|
− nπ Z1 |
sin |
|
2 |
|
dx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπx |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
cos |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
nπ h2 sin(nπ) − sin |
2 |
|
i |
|
n2π2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
= |
|
|
|
|
h0 − sin |
|
|
|
i + |
|
|
hcos(nπ) − cos |
|
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
nπ |
|
2 |
|
n2π2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
= |
|
2 |
|
|
sin |
nπ |
+ |
|
|
4 |
|
h(−1)n − cos |
nπ |
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
− |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
nπ |
|
2 |
|
|
n2π2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nπ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
an |
= |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(−1)n − cos |
|
|
|
|
− sin |
|
|
|
|
n = 1, 2, . . . |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
nπ |
nπ |
|
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Then,
|
a0 |
∞ |
nπx |
|
|
|
f (x) = FC (x) = |
+ n=1 an cos |
|
for 0 < x < 2 |
|||
2 |
L |
|||||
|
|
X |
|
|
|
f (x) = |
3 |
+ |
2 ∞ 1 |
2 |
(−1)n − cos |
|
nπ |
− sin |
|
nπ |
cos |
|
nπx |
|
0 < x < 2 |
|
4 |
π n=1 n |
nπ |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
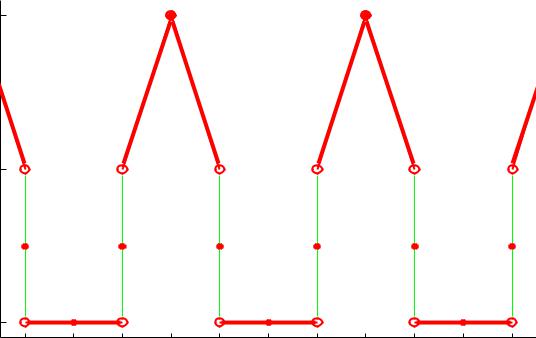
Fourier Cosine Series representation of f(x)
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FC (x) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-5 |
-4 |
-3 |
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
|
|
|
|
Notice that all three series converge to f (x) over the interval (0, 2), except at the point of discontinuity. However, the convergence of the three series di er outside of this interval.
