
- •1. Kazakhstan – Trivia
- •2. The main landscape zones in Kazakhstan
- •3. The major ecological problems in Kazakhstan
- •4. The main factors of desertification in Kazakhstan
- •5. Water problems in Kazakhstan
- •International agreements have addressed the water allocation issues between Kazakhstan and its neighbors
- •6. Biodiversity loss problems in Kazakhstan
- •7. Ecological legislation in Kazakhstan
5. Water problems in Kazakhstan
The main reason of the Aral Sea catastrophe is: careless use of water for irrigation
Some data about the Aral sea changes (from 1960s to 1990s -2000s):
The salt concentration of the Aral sea water increased to 3–5 times.
The surface area of the Aral sea decreased to 50 -75%
The water level of the Aral sea fell to 16-18 meters.
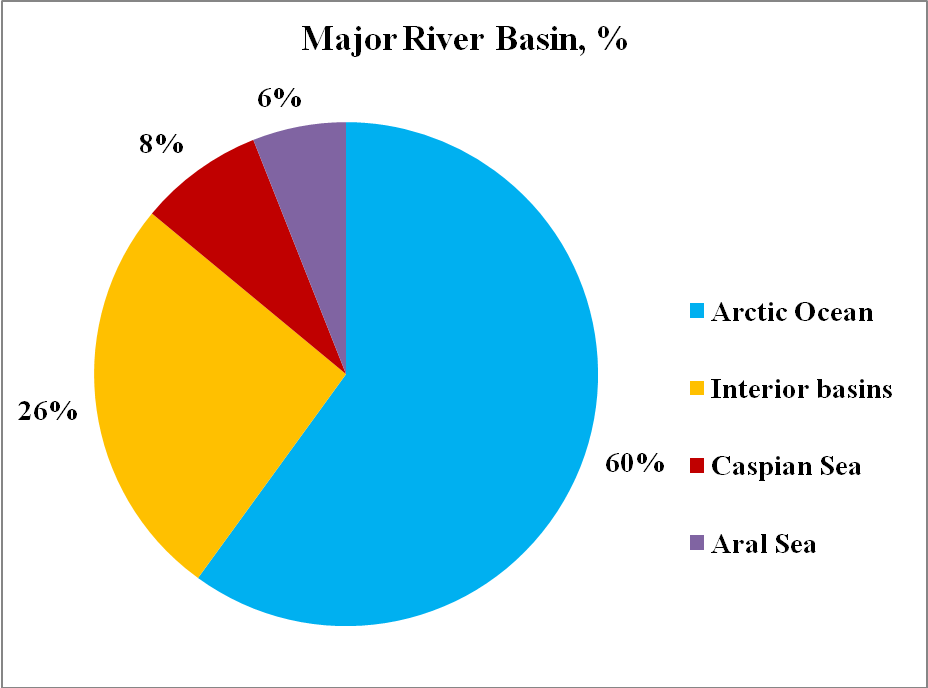
Four major hydrologic regions can be distinguished in Kazakhstan, depending on the final destination of water: the Arctic Ocean through the Ob River, the Caspian Sea, the Aral Sea and internal lakes, depressions, or deserts
During last years water problems connected basically with surface waters resources decrease were considerably aggravated in Kazakhstan.
The main reason – decrease of discharge from neighboring states of transboundary rivers of Irtysh, Ile, Syrdarya, Ishim, Tobol, Ural, Talas, Shu
International agreements have addressed the water allocation issues between Kazakhstan and its neighbors
For the Syr Darya River, the existing principles governing water sharing among the Central Asian countries will remain valid (Agreement of 18 February 1992) until the adoption of a new water strategy for the Aral Sea basin, endorsed by the Interstate Commission for Water Coordination. Under the 1992 Agreement, the part of the Syr Darya surface water resources allocated to Kazakhstan has to be no less than 10 km3/year downstream of the Chardara reservoir. Considering the 4.5 km3/year of internal surface water resources generated in the Kazakh part of the Syr Darya River basin, it can be considered that the actual surface water resources in the Kazakh part of the Syr Darya basin are about 14.5 km3/year.
For the Chu and Talas rivers, flowing in from the Kyrgyz Republic, an interstate agreement has been reached with the Kyrgyz Republic (May 1992). This agreement addresses the water allocation issues between both republics, considering the total resources generated in the basin (including surface water, groundwater, and return flow) and taking into account the water evaporated from the lakes and reservoirs. On average, it can be considered that the part of the surface water resources allocated to Kazakhstan is 1.24 km3/year for the Chu basin and 0.79 km3/year for the Talas and Assa river basins.
6. Biodiversity loss problems in Kazakhstan
The total area of the Particularly Protected Natural Territories (PPNT) in Kazakhstan is more than 14,5 mln ha, or about 5,3 % of the republic territory.
Country |
Protected territories, % |
Australia |
15 |
Turkmenistan |
10 |
J Norway |
9.2 |
US |
3.3 |
Russia |
3 |
Canada |
1.5 |
Kazakhstan |
0.5 |
There is high level of diversity of flora (more than 6000 species of vascular plants) and fauna (835 species of vertebrates and more than 50 000 of species of invertebrates) in Kazakhstan.
More than 404 species of plants and 309 species of animals require protection (endangered species) and are included into the Red Data Book of Kazakhstan.
Zapovedniks (Reserve or Refuge) – unchanged or weakly changed by human natural complexes with the strict prohibition of any economic and recreation activity to protect and study their wildlife.
№ |
Name |
Foundation |
Area, thousand ha |
Oblast |
Protected landscapes |
Natural zones |
1 |
Aksu-Jabagly |
1926 |
85,6 |
South Kazakhstan |
Mountain forests |
Mountain |
2 |
Almaty |
1960 |
71,7 |
Almaty |
Mountain forests |
Mountain |
3 |
Barsa-kelmes |
1960 |
71,7 |
Kyzylorda |
Desert |
Desert |
4 |
West Altay |
1922 |
56,1 |
East Kazakhstan |
Mountain forests |
Mountain |
5 |
Korgalzhin |
1968 |
252,3 |
Akmola |
Wetland |
Steppe |
6 |
Markakol |
1976 |
75,0 |
East Kazakhstan |
Mountain forests |
Mountain |
7 |
Naurzum |
1931 |
87,7 |
Kostanay |
Lake, steppe, forest |
Steppe |
8 |
Ustyurt |
1984 |
223,3 |
Mangistau |
Desert |
Desert |
9 |
Alakol |
1998 |
12,5 |
Almaty |
Wetland |
Semi-Desert |
10 |
Karatau |
2004 |
34,3 |
South Kazakhstan |
Mountain forests |
Mountain, Forests-steppe |
National parks – large areas with restricted human economic and recreation activities to protect and study their wildlife.
№ |
Name |
Foundation
|
Area, thousand ha |
Oblast |
Protected landscapes |
Natural zones |
1 |
Bayanaul |
1985 |
50,7 |
Pavlodar |
Melkosopochnik (hills) (lakes, pine forest) |
Steppe |
2 |
Ile-Alatau |
1996 |
165,4 |
Almaty |
Mountain (alpine coniferous forest) |
Mountain |
3 |
Kokshetau |
1996 |
135,8 |
Akmola |
Forest-steppe (pine forests, lakes, steppes) |
Forest-steppe |
4 |
Altyn-Emel |
1996 |
209,6 |
Almaty |
Desert (rocky, sandy) |
Desert |
5 |
Karkaraly |
1998 |
90,3 |
Karaganda |
Steppe (pine forests, lakes, steppes) |
Steppe |
6 |
Burubay |
2000 |
84,1 |
Akmola |
Forest-steppe (pine forests, lakes, steppes) |
Mountain |
7 |
Katon-Karagay |
2001 |
643,5 |
Kostanay |
Lake, steppe, forest |
Forest-steppe |
8 |
Kolsay Lakes |
2004 |
10,3 |
Almaty |
Lake, forest |
Mountain |
9 |
Sayram-Ugam |
2004 |
12,5 |
South Kazakhstan |
Forest-steppe |
Semi-desert |
10 |
Charyn |
2004 |
149,8 |
Almaty |
Steppe, semi-desert |
Semi-desert |
11 |
Zhongar-Alatau |
2010 |
356.0 |
Almaty |
Mountain, Forests |
Mountain |
12 |
Buyratau |
2011 |
89.0 |
Akmola-Karaganda |
Steppe, Forests |
Steppe |
Zakazniki
The territories is created to protect the populations and landscapes without exception of the soils from the industrial process, but with the regulations of the economic activity.
There are 57 zakazniks in Kazakhstan.
They are divided into 4 types:
Zoological — 63 %
Botanical — 23 %
Complex — 12 %
Botanical-geological — 2%
Nature Heritage Sites
In Kazakhstan there are 26 republican and 53 oblast Heritage Sites.
Botanical Gardens
Main Botanical Garden (Almaty)
Altay Botanical Garden (Ridder)
Zhezkazgan Botanical Garden (Zhezkazgan)
Ili Botanical Garden (Almaty oblast)
Mangyshlak Botanical Garden (Aktau)
Zoos
There are 3 zoos in Kazakhstan:
Almaty
Karaganda
Shymkent
According to the “Concept of the PPNT development and creating in Kazakhstan up to 2030 year”, approved by the Government of RK in 2000, it is proposed to increase the area of these territories up to 17,490 thousand ha (6,4 % of the republic territory).
It is proposed to create 13 State National Parks and 25 State Reserves (zapovedniks).
With the assistance of some International Organizations it is planned to create 6 Biosphere reserves with the total area of 670 thousand ha.
