- •УЧебное пособие по английскому языку
- •Введение
- •Содержание
- •Infinitive
- •Unit 5 43
- •Air pollution and smog are the problems of modern cities
- •1.Translate these word combinations and make a dialogue.
- •2. Read three given jists of the text and find one which corresponds to the contents best.
- •3. One of the greatest problems of all modern cities is the environment pollution. Read the text and tell which of the problems mentioned in the text are typical for the city you live in.
- •4. Give the summary of the text.
- •Air pollution as the major problem of the day
- •1. Say if the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements.
- •2. What environmental problems does air pollution cause? Fill in the table.
- •3. You are taking part in the conference on the environmental problems. Deliver a report on air pollution.
- •The ozone layer depletion
- •Страдательный залог (passive voice )
- •Organic chemistry
- •Chemical elements and compounds
- •Organic compounds
- •Substances and their transformations
- •Страдательный залог с модальными глаголами
- •Industrial Gases
- •An achievement of science: gas transformed into metal
- •Инфинитив (the infinitive)
- •Частью сказуемого:
- •Unit 4 units materials science and technology
- •Mechanical properties of materials
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary
- •Объектный инфинитивный оборот (the objective infinitive construction)
- •Measuring temperature
- •Субъектный инфинитивный оборот
- •(The subjective infinitive construction)
- •Ventilation : definition and necessity
- •Functional requirements of ventilationsystem
- •1. Air changes (or air movement) and rate of supply of fresh air
- •Systems of ventilation
- •Natural ventilation
- •Fig. 2.1. Movement of wind through buildings.
- •Ventilation due to stack effect
- •Fig. 2.4. Ventilation due to stack effect.
- •Ventilation due to both the effects
- •Meciianical (or artificial) ventilation
- •1. Extraction system (or exhaust system)
- •2. Plenum system (or supply system)
- •3. Extraction-Plenum system
- •4. Air conditioning
- •Air conditioning
- •Vocabulary
- •Герундий (gerund)
- •2. Сhoose suitable English words to Russian terms. Make your own sentences.
- •3. Read the text. Mark which paragraphs devote to the title of the text
- •4. Find correct Russian translation of English words. Compose sentences with them on the topic of the text. Find unnecessary words
- •5. Define which of these statements contain the main idea of the text
- •6.Put these sentences in order according to the text
- •7. Find the correct answer to these questions. Prove your opinion
- •8. Which paragraphs deal with these questions? Give brief explanations to each of them
- •9. Which of these sentences explain the work of heating and which ones -ventilation?
- •10. Prove these statements, add some more information from the text
- •11. Compose pairs of words from English and Russian synonyms. Explain their meaning
- •12. Read the text. Mark which paragraphs devote to the title of the text
- •14. Mark which paragraphs these titles belong to. Place them in order according to the text
- •15. Finish these sentences
- •16. Divide these sentences into three groups
- •18. Change these words into another part of speech
- •Причастие (the participle)
- •§ 217. 1. Present Participle Active (причастие настоящего времени
- •1.Переведите на русский язык, обращая внимание на причастия.
- •2. Translate the following word-combinations in accord to the given models:
- •3.Замените придаточные предложения причины причастными оборотами.
- •4.Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Present Participle или Perfect Participle.
- •I. Tasks before reading.
- •II. Listen to the students' discussion and name advantages and disadvantages of alternative energy sources
- •III. Complete the following dialogues.
- •IV. Match a line in a with a line in b.
- •Vocabulary
- •I. Match the English words with their Russian equivalents.
- •II. Match the words with the opposite meaning.
- •III. Find in в the derivatives from the words in a.
- •I. What do we need energy for? Make a list of the uses of energy and compare it with that of your partner.
- •II. Translate the following compound nouns into Russian.
- •III. Scan the text to find answers to these questions.
- •Forms of energy
- •Varieties of energy (a)
- •The end of the universe (b)
- •Heat energy (c)
- •Participle II
- •Независимый причастный оборот (the absolute participle construction)
- •1. Express the same idea in a shorter way.
- •2. Join these sentences into one.
- •3. Provide more detailed information.
- •4. Expand the sentences.
- •5. Choose the right option.
- •6. Open the brackets and use Participles in the right form.
- •7. Correct mistakes.
- •Water supply
- •1. Choose suitable translation of English words from Russian ones. Compose sentences with them on the topic of the text
- •2. Chose the translation of bold type (выделенных) words.
- •3.Point which of these sentences have the main idea of the text. Explain your point of view
- •4. Which of these statements contain the basic of the text. Put them in accordance with the context
- •5. Add these sentences with correct variant according to the text. Using as a plan speak briefly about Water Supply
- •6. Fill this table due to points of the topic Sanitary engineering
- •Unit 10
- •Operating systems
- •Vocabulary:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Introduction to the www and the internet
- •Vocabulary:
- •Famous people of Science and Engineering. Bill gates
- •Unit 11
- •2. Chilled Water System
- •2.9. Essentials of air conditioning system
- •1. Filtration
- •2. Heating
- •3. Cooling
- •4. Humidification
- •5. Dehumidification
- •6. Air circulation or distribution
- •Unit 12 albert einstein
- •Time for fun
- •Unit 13 mstislav keldysh (1911-1978)
- •Industrial plastics: rigid and flexible foams
- •Unit 14
- •D.I. Mendeleyev — pride of russian science
- •Unit 15
- •Igor kurchatov (1903—1960)
- •Unit 16 our star —the sun
- •Список литературы
Unit 11
Direct Expansion (DX) systems
Chilled water (indirect) systems. 1. Direct Expansion System
It is the system where the refrigerant is utilised to cool the air directly. The common examples of this system are :
Room air conditioner.
Packaged units.
Central direct expansion plants.
The main components of the direct expansion system are :
(i) Compressor (hermetic or open type).
(ii) Condenser (air cooled or water cooled).
(iii) Evaporater or cooling coil with fan.
(iv) Cooling tower or spray panel (in case of water-cooled condensor)
(v) Condenser water pump set.
(vi) Air distribution ducting and grills.
Room air conditionrs
There are self-contained air conditioning units, comprising of a compressor, evaporator fan and air-cooled condenser. This type of plant is used for single rooms having limited occupancy. These units are ideally suited for bed rooms and rooms of similar application, where very close control of temperatures and relative humidity is not required. Room air conditioner is mounted at the window sill on an external wall where hot air from the condenser can be discharged without causing a nuisance.
Packaged air Conditioners
Packaged air conditioner comprises of a compressor, water cooled condenser, evaporator and fan, all mounted in a sheet metal cabinet. They are ideally suited for residences, shops, banks, offices and some industrial applications. Window units are available upto a limited capacity. For higher capacity it is economical to operate the air-cooled window system and the equipment also becomes bulky, which does not make if possible to install it at the window. Floor mounted self-contained packaged units are made to meet the requirements for large capacities. The packaged units can be mounted within the air-conditioned space or remote in a separate enclosure. The installation becomes economical if the unit is mounted within the space. They are normally mounted on a resilient pad which prevents vibration of the compressor from being transmitted to the building.
Central direct expansion plants
In this system, all the equipment pertaining to air conditioning is installed in a central plant room, and the conditioned air is distributed to the rooms/halls/enclosures by ducts. The system is more useful for factories, hotels, assembly halls, cinema halls and big residential buildings where it is uneconomical to install separate units for each room.
2. Chilled Water System
In this system, secondary medium, such as water is used to cool the air. The refrigerant first cools the water and then the water cools the air. The main components of this system are the same as direct expansion system but a chiller is the additional item. Following is the list of the components of the system :
(i) Compressor (reciprocating or centrifugal),
(ii) Condenser (mostly water-cooled).
(iii) Chiller (direct expansion or flooded type).
(iv) Air handling unit with chilled water coil and/or fan coil unit or chilled water air washers.
(v) Cooling tower.
(vi) Chilled water and condenser water pump sets.
(vii) Air distribution ducting and grills.
Chilled water is produced in the refrigeration plant housed in the main plant room. Chilled water is then carried through insulated chilled water piping to air-handling unit or fan coil unit, where the return-air and the fresh-air mixture is filtered, cooled and dehumidified and' then distributed to the conditioned space through galvanized iron and aluminium ducting and grills/diffusers. The return air is brought back to the air-handling unit through the annular space formed around the supply air duct and the false ceiling enclosure. Here it is mixed with the fresh air or ventilation air and then passed through the filters and the cooling coil.
Selection of air-conditioning system
The selection of correct air-conditioning system for a particular building depends upon the following factors :
(i) Capital cost.
(ii) Running and operating cost.
(iii) Space for the location of the equipment.
(iv) Type of application : Whether comfort application or
industrial application.
(v) Type of controls required : Whether rigid control on
the inside of the conditioned space is required as in
the case of some industrial applications.
(vi) Acoustic considerations, such as in auditoriums, radio
and TV studios, conference rooms, etc.
(vii) Type of filtration, whether sterile room or clean room
application.
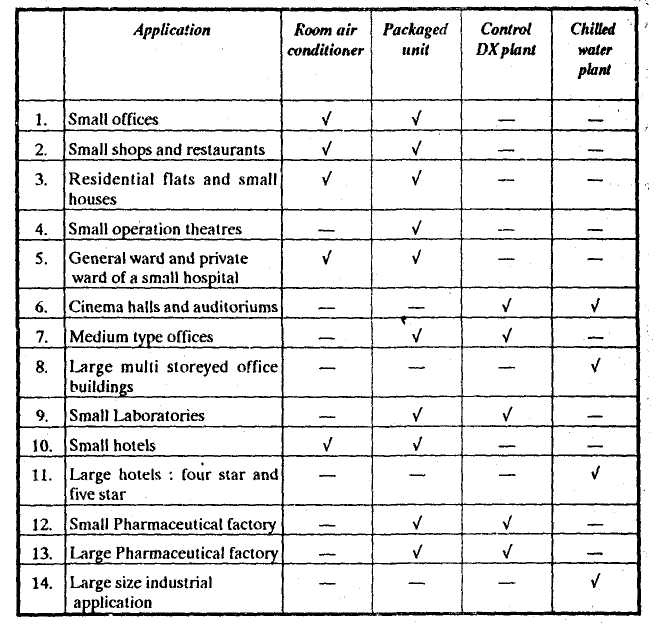
Table 2.2 gives general guidelines for the selection of proper air conditioning system for various applications. In the table, v7 indicates the recommonded type of air conditioning system.
TABLE 2.2. SELECTION OF AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM