
- •Раздел 1. В Офисе At the office
- •Тема 1.1 Знакомство Acquaintance
- •3.Выполнить упражнения № 9,10.
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 1.1.1, 1.1.2., 1.1.3
- •In the Office
- •Eye contact
- •Read my Lips
- •Тема 1.2 Условия для трудовой деятельности Conditions for labor activity
- •4. Выполнить упражнения № 4-7
- •5. Прослушать текст и выполнить задания (упр. 2-3, 9)
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №1,2,5,9.
- •4. Выполнить упражнения № 1, 2, 5, 6, 7
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 1.2.1, 1.2.2.,1.2.3
- •T he active workplace
- •What to wear to get that job?
- •Office fire safety tips
- •If you are unable to evacuate
- •Тема 1.3. Должности и взаимоотношения; корпоративная культура Posts and interrelations; corporate culture
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №1-4
- •5. Прослушать текст и выполнить задания (упр. №2)
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №21-22
- •3. Выполнить упражнения №33-35
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 1.3.1.,1.3.2.,1.3.3.
- •Ford of britain
- •Bic’s success in a throwaway world Bic is a household name, synonymous with a disposable age.
- •Company history
- •Office workers “admit being rude”
- •Admit avoid ignore introduce invest improve respond
- •Раздел 2. Планирование рабочего и свободного времени Planning of working time and free time
- •Тема 2.1. Рабочий день Working day
- •Выполнить упражнения №1-3
- •Выполнить упражнения №1-3
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 2.1.3
- •Part-time Job, full-time benefit
- •World of work. Do we live to work or work to live
- •Тема 2.2. Развлечения Entertainment
- •4.Выполнить упражнения №1-3, 6, 9, 10
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №1-6, 11
- •5. Прослушать текст и выполнить задания (упр. № 12)
- •4.Выполнить упражнения № 7,14-20
- •5.Прослушать текст и выполнить задания (упр. № 8)
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Тема 2.3. Отпуск Holiday
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №4-11
- •The weather
- •Vocabulary Commentary
- •Your checklist for travelling abroad
- •Раздел 3. Особенности питания в России и за рубежом Nutrition peculiarities in Russia and abroad
- •Тема 3.1. Магазины и покупка продуктов Shops and buying products
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3
- •Step 2. Summarise the results (%) Step 3. Display them for the whole class.
- •Britain’s Young Consumers
- •Ex 7. Listen to the conversation between two friends and mark the statements as true (t) or false (f).
- •Your problems... Solved!
- •Coca-Cola and its advertising
- •Тема 3.2. Деловой ужин Business Dinner
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 3.2.1, 3.2.2, 3.2.3
- •British Cuisine
- •A brief history
- •The Great British Breakfast!
- •Independent work
- •Ex 7. Fill in the gaps with much or many.
- •Ex 8. Fill in the gaps with little or few.
- •Ex 9. Fill in the gaps with little, a little, few or a few.
- •Ex 3. In pairs, act out similar dialogues on the topic “How To Choose a Restaurant” Use phrases from the list below. How To Choose a Restaurant
- •Independent work
- •10 Tips for showing good manners over lunch or dinner
- •Тема 3.3.Традиции русской и других национальных кухонь Traditions of Russian and other national cuisines учебно-методическая карта занятия № 3.3.1
- •Учебно-методическая карта занятия № 3.3.2
- •Учебно-методическая карта занятия № 3.3.3
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 3.3.1, 3.3.2, 3.3.3
- •Vocabulary Practice
- •Peculiarities of national british cuisine
- •Vocabulary Practice
- •Tastes are different
- •American food and their manner of eating
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Russian Cuisine Recipes
- •Vegetable Okroshka recipe
- •British Cuisine Recipes
- •Раздел 4. Составляющие имиджа специалиста Components of a specialist’s image
- •Тема 4.1. Стили одежды Wearing styles
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №3-5
- •5. Прослушать текст и выполнить задания (упр. №18)
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №12-14
- •4. Выполнить упражнения №15-17
- •5. Прослушать текст и выполнить задания (упр. №11)
- •Научиться переводить на родной язык письменные и устные неофициальные и официальные приветствия друзей, коллег, работающих в различных учреждениях за рубежом
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 4.1.1, 4.1.2, 4.1.3
- •What Is the Business Professional Dress Code?
- •Vocabulary practice
- •A Short History of Youth Street Fashion
- •Trendy occupations: What are the really fashionable doing to earn their living
- •What clothes do people wear in Britain?
- •Тема 4.2. Покупка одежды Buying clothes
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 4.2.1, 4.2.2, 4.2.3
- •Seasonal clothes for women
- •Vocabulary booster
- •Shop till you drop
- •At the clothes shop
- •Тема 4.3. Создание имиджа Image creating
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 4.3.1, 4.3.2, 4.3.3
- •Image Making
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Clothes count for first impressions only
- •Body Language
- •Types of nonverbal communication and body language
- •Worries about Physical Appearance
- •Define your style
- •Раздел 5. Молодежь в России и за рубежом Young people in Russia and abroad
- •Тема 5.1. Система образования в России, Англии и сша. Educational system in Russia, England and the usa
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 5.1.1, 5.1.2, 5.1.3
- •My School Day
- •The british educational system
- •Our University (a Letter)
- •Тема 5.2. Социальные проблемы молодежи Social problems of young people
- •3. Выполнить упражнения № 6-8
- •2. Выполнить упражнения № 1-3
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 5.2.1, 5.2.2, 5.2.3
- •Vocabulary
- •Natasha’s story
- •Ecstasy, Euphoria… and Death
- •Тема 5.3. Увлечения молодёжи Passions of young people
- •4. Выполнить упражнения № 4-6.
- •3. Выполнить упражнения № 4-6.
- •3. Выполнить упражнения № 3, 4.
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 5.3.1,5.3.2,5.3.3
- •Extreme sports
- •Music in our life
- •Enrico Caruso
- •Раздел 6.Здоровьесберегающие технологии. Health keeping technologies
- •Тема 6.1. Вредные привычки. Harmful habits
- •If you had a big problem like Victoria, who would you ask for help?
- •Are you hooked?
- •Тема 6.2. Охрана окружающей среды Environmental protection
- •Дидактический материал к занятиям 6.2.1, 6.2.2, 6.2.3
- •Enviro-Myths You Can Stop Believing
- •Why We're Destroying the Earth
- •Тема 6.3. Безопасность на производстве Safety at the factory
- •4. Выполнить упражнения № 1 - 4
- •Выполнить упражнения №4 - 7
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 6.3.1,6.3.2, 6.3.3
- •Stress at Work
- •Vocabulary
- •Stressed
- •Ex 21. Read the article about office accidents and write a report about their reasons and ways to avoid them. Lesson 6.3.2. Office Accidents
- •Preventing office injuries
- •Causes of office accidents
- •Ex 4. Give some advises to your friend how to Preventing office injuries.
- •Health and Safety
- •Health and Safety at Work
- •Health and Safety Claims and Industrial jobs
- •Health and safety in public places
- •Раздел 7. Современные технологии Modern technologies
- •Тема 7.1. Технические инновации в повседневной жизни Technical innovations in everyday life
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 7.1.1,7.1.2, 7.1.3
- •The digital age
- •Wahing machine instruction
- •Тема 7.2. Современные средства коммуникации: электронная почта, мобильный телефон, компьютер. Modern means of communication: e-mail, mobile phone, computer.
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 7.2.1,7.2.2, 7.2.3 Modern means of communication: email, mobile phone, computer.
- •Computers Make the World Smaller and Smarter
- •No mobile phones at school
- •Тема 7.3. Современные средства коммуникации: электронная почта, мобильный телефон, компьютер. Modern means of communication:email, mobile phone, computer.
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 7.3.1,7.3.2, 7.3.3
- •Dawn of the Cyberbabes.
- •What is Biotechnology?
- •Cloning of a Ewe ( The Roslin Method)
- •8.Clusters of embryonic cells
- •9.A surrogate mother
- •Раздел 8. Профессии и карьера Profession and career
- •Тема 8.1. Техническое и гуманитарное образование в России и за рубежом Technical and humanitarian education in Russia and abroad
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 8.1.1,8.1.2, 8.1.3
- •Mine surveying
- •Chemical technology for natural fuels and carbon materials
- •Power stations
- •Insulation, cable and capacitor engineering
- •Cooperative Kids
- •Vocabulary Practice
- •Cambridge University
- •Higher education
- •Тема 8.2. Специфика профессии.
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 8.2.1,8.2.2, 8.2.3
- •Living by the Sword
- •Vocabulary practice
- •What is a manager?
- •Management qualities
- •Income: Wage vs Salary
- •Тема 8.3. Поиск работы и продвижение по службе.
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 8.3.1,8.3.2, 8.3.3
- •On the job market
- •Resume as it is
- •Job interview
- •Раздел 9. Международное сотрудничество International collaboration
- •Тема 9.1. Деловая поездка за рубеж Business trip abroad
- •Дидактический материал для занятий 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3.
- •British Visas (Part 1)
- •Vocabulary practice
- •British Visas (Part 2).
- •Coverage for Hospital Treatment
- •Arriving in the uk (Passport Control and Customs)
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Hubs and spokes
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Тема 9.2. Деловые контакты с зарубежными партнерами. Business contacts with foreign partners
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 9.2.1,9.2.2, 9.2.3
- •Vocabulary
- •Check-in at a Hotel
- •Hotel Information
- •Hotel Lobby
- •Hotel Problems
- •Complaints
- •Room service
- •Check-Out
- •Presentations
- •U.S. Plans Fellowships for Graduate Students
- •Vocabulary
- •When egOs* collide: In the acquisitions jungle, alpha* males are deal-breakers
- •Vocabulary
- •Тема 9.3. Прием зарубежных партнеров в России
- •Дидактические материалы к занятиям 9.3.1,9.3.2, 9.3.3
- •How to Plan a Business Tour
- •Meeting at the airport
- •Sun tours: Short breaks in New York
Ford of britain
When did all start?
In the spring of 1896 engineer Henry Ford built his first horseless carriage. In 1903 Ford, backed by 12 local business men, formed the Ford motor company which later pioneered modern production line techniques.
When did it come to Britain?
In 1911 Ford’s first assembly plant outside North America opened at Trafford Park, Manchester and in 1929 work started on building the Dagenham plant where the first Model AA truck rolled off the line at 1.15 p.m. on October 1, 1931.
Ex 14.What do these numbers from the text refer to?
1903, 1929, 12, 1896, 1931, 1911
Ex 15. Complete these sentences.
1. In 1896 Henry Ford........... his first car.
2. In 1903 Henry Ford .... the Ford Motor Company.
3. Twelve local businessmen ..................him.
4. In 1911 Ford............. the first assembly plant in Manchester, England.
5. In 1929 he...........building the Dagenham plant.
Ex 16. Answer these questions about the past simple tense.
1. How is the reqular past simple tense formed? e.q, started, backed, opened
2. Not all verbs have a regular past simple tense. Give an example of an irregular past simple tense from the text.
3. Look at the two questions (a and b). Underline the auxiliary verb ~
and the main verb ----- for each.
a) When did it all start?'
b) When did it come to Britain?
4. Look at the two negative sentences and underline the negative auxiliary verb
and the main verb ------------- for each:
Ford built the first car in 1896, but he did not form the company until 1903. The first truck didn't roll off the line until 1931.
Lesson 1.3.2. Company and its production
Ex 1. Read the information about company structure and draw a chart.
Most companies are made up of three groups 'of people: the shareholders (who provide the capital), the management and the workforce. The management structure of a typical company is shown in the organisation chart.
At the top of the company hierarchy is the Board of' Directors, headed by the Chairperson or President. The Board is responsible for policy decisions and strategy. It will usually appoint a Managing Director or Chief Executive Officer, who has overall' responsibility for the running of the' business. Senior managers or company officers head the various departments or functions within the company, which may include the following: '
a Marketing e Finance
b Public Relations f Production
c Information Technology or IT g Research and Development or R and D d Personnel or Human Resources'
Ex 2. Match the company departments (1-6) with the words below.
1. Human Resources a. accounting reports
2. Production b. future products
3. Marketing c. hiring staff
4. Information Technology d. sales
5. Finance e. factory, workshop
6. Research and Development f. Computers
Ex 3. Work in pairs. Say what you know about the companies in the table.
|
Virgin |
United colors of benetton |
Daimler chrysler |
Sony |
Nationality |
|
|
|
|
Product(s) |
|
|
|
|
Other information |
|
|
|
|
Ex 4. Tom Armstrong and Rachel Humphries talk about the four companies. Listen and complete the table.
Ex 5. Look at the three company organigrams. How are these organizations different from each other?
Business units

Functional organization
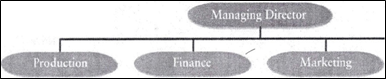
Parent company/subsidiary
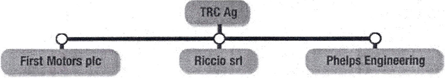
Ex 6. Listen to Petra Wilson who is talking to employees from the three different companies in 1 about their organizations. Which organigram are they describing?
Speaker 1....... Speaker 2........ Speaker 3........
Listen to part 1 again. How was the company organized in 1996?
Listen to part 2 again, Who changed the organization?
Listen to part 3 again. Why does the company have a traditional organization?
Ex 7. The text is about the French company, Bic. Can you name three of Bic's products? What are the advantages of disposable or 'throwaway' products? Now quickly read the text to check.
