
- •Содержание
- •Реферат
- •Введение
- •Постановка задачи
- •Операционный автомат
- •Объединенная граф схема алгоритма
- •2. Проектирование операционного автомата
- •3. Проектирование управляющего автомата
- •4. Проектирование процессорного модуля
- •4.1 Схема объединения операционного и управляющего автоматов
- •4.2 Результаты тестирования
4. Проектирование процессорного модуля
4.1 Схема объединения операционного и управляющего автоматов

Рис. 4.1 – Схема объединения операционного и управляющего автоматов
4.2 Результаты тестирования
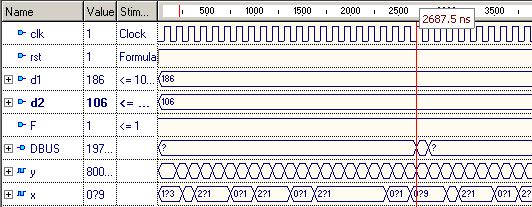
Рис. 4.2.1 – Результат умножения двух беззнаковых чисел

Рис. 4.2.2 – Результат деления знаковых чисел без восстановления остатка
ВЫВОД
Данный курсовой проект разработан для изучения современных средств проектирования цифровых вычислительных машин. В этом проекте был разработан двухуровневый процессорный модуль, который был спроектирован на основе управляющего автомата типа П с принудительной адресацией и операционного автомата класса I. С помощью данного устройства можно выполнять такие микрооперации, как сложение, умножение и деление двоичных знаковых и беззнаковых чисел. П-автомат является автоматом с программируемой логикой. Для таких автоматов затраты оборудование больше (при несложных микрокомандах), чем в автоматах с жесткой логикой. Чем сложнее микропрограмма, тем меньше аппаратные затраты.
Управляющие автоматы и автоматы с жесткой логикой отличаются степенью гибкости. Для автоматов с жесткой логикой, при возникновении ошибки в микропрограмме, необходимо перестраивать структуру автомата. Программируемая логика позволяет решить задачу перестройки структуры относительно просто – путем прошивки в ПЗУ дополнительных микрокоманд, изменяемых при внесении изменений в микропрограмму. Таким образом, можно считать, что гибкостью обладают только автоматы с программируемой логикой.
СПИСОК ИСПОЛЬЗУЕМЫХ ИСТОЧНИКОВ
Майоров С.А., Новиков Г.И., Структура электронных вычислительных машин. - Л.: Машиностроение. Ленингр. Отделение, 1979. - 384 с., ил.
Баранов С.И., Скляров В. А., Цифровые устройства на программируемых БИС с матричной структурой. - М.: Радио и связь,
1986. - 272 с, ил.
Угрюмов Е.П., Проектирование элементов и узлов ЭВМ: Учеб. Пособие для спец. ЭВМ вузов. - М.: Высш. шк., 1987. - 318 с, ил.
ДСТУ 3008-95. «Звіти у сфері науки і техніки. Структура та правила оформлення».
ПРИЛОЖЕНИЕ А
Листинг программы
---------------
-- unit.vhd
---------------
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.all;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_unsigned.all;
entity OU is
generic (n:natural:=8);
port( -- n = 8
clk,rst:in std_logic;
d1:in std_logic_vector(2*n-1 downto 0);
d2:in std_logic_vector(n-1 downto 0);
f:in std_logic;
y:in std_logic_vector(24 downto 1);
x:out std_logic_vector(10 downto 1);
DBUS:out std_logic_vector(2*n-1 downto 0)
);
end OU;
--}} End of automatically maintained section
architecture OU of OU is
--use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
signal A:std_logic_vector(2*n-1 downto 0);
signal B:std_logic_vector(n downto 0);
signal C:std_logic_vector(n downto 0); --Po GSA 7
signal CnT:std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
--signal CnTu:std_logic_vector(2 downto 0);
signal TgS,IRQ1,IRQ2:std_logic;
--signal stop:std_logic:= '0';
begin
process (clk,rst) is
begin
if rst='0' then A <=(others=>'0');
B <=(others=>'0');
C <=(others=>'0');
Cnt <= "1000";
-- CnT <= "111";
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
if y(1)='1' then A <= d1;
elsif y(19)='1' then A <= ("00000000" & d1(n-1 downto 0));
elsif y(5)='1' then A(2*n-1 downto n-1) <= IEEE.std_logic_signed."+"(A(2*n-1 downto n-1), (not B));
A(2*n-1 downto n-1) <= IEEE.std_logic_signed."+"(A(2*n-1 downto n-1),1);--****
elsif y(6)='1' then A(2*n-1 downto n-1) <= IEEE.std_logic_signed."+"(A(2*n-1 downto n-1), B);
elsif y(12)='1' then A <= (A(2*n-2 downto 0) & '0');
elsif y(13)='1' then A <= IEEE.std_logic_signed."+"(A,(not B));
A <= IEEE.std_logic_signed."+"(A,1);
elsif y(14)='1' then A <= IEEE.std_logic_signed."+"(A,B);
end if;
if y(2)='1' then B <= (d2 & '0');
elsif y(20)='1' then B <= ('0' & d2);
elsif y(4)='1' then B <=(B(n) & B(n downto 1));--B <= B(8) & B(7 downto 0);-- B <= '0' & B(8) & B(8 downto 2);
elsif y(22)='1' then B <= '0' & C(0) & B(n-1 downto 1); --B <= '0' & C(0)&B(6 downto 0);--B <= '0' & C(0)& '0'& B(7 downto 2);
end if;
if y(7)='1' then C <=(others=>'0');
elsif y(9)='1' then C <= '0'&C(n-2 downto 0)&'1'; --elsif y(9)='1' then C <= C(n-1 downto 0) & '1';
elsif y(10)='1' then C <= '0'&C(n-2 downto 0)&'0'; --elsif y(10)='1' then C <= C(n-1 downto 0) & '0';
elsif y(15)='1' then C <= IEEE.std_logic_signed."+"(C,1);
elsif y(21)='1' then C <= IEEE.std_logic_unsigned."+"(C,'0'&A(n-1 downto 0)); --sm <= sm + 1;--sm <= IEEE.std_logic_unsigned."+"(('0'& C),A(7 downto 0));--C + A(7 downto 0); sm <= ('0'& C) + A(7 downto 0);
elsif y(23)='1' then C <= '0'& C(n downto 1);--C <= '0' & C(7 downto 1);
end if;
if y(8)='1' then CnT<="1000";
elsif y(11)='1' then CnT <= CnT - 1;
end if;
if y(3)='1' then TgS <= A(2*n-1);
end if;
if y(17)='1' then IRQ1 <= '1'; assert (0>1) report "IRQ1 was thrown" severity failure ;
elsif y(18)='1' then IRQ2 <= '1'; assert (0>1) report "IRQ2 was thrown" severity failure ;
end if;
end if;
end process;
-- IRQ1 <= '1' when y(16)='1';--assert (0>1) severity failure;
-- IRQ2 <= '1' when y(17)='1';--assert (0>1) severity failure;
DBUS <= C(n-1 downto 0) & B(n-1 downto 0) when y(24)='1'else
--DBUS <=
"00000000" & C(n-1 downto 0) when y(16)='1' else (others=>'Z');
x(1) <= f;
x(2) <= '1' when B = "000000000" else '0';
x(3) <= A(2*n-1) xor B(n);
x(4) <= '1' when CnT = "000" else '0';
x(5) <= A(2*n-1) xor TgS;
x(6) <= B(n);
x(7) <= B(n) xor TgS;
x(8) <= TgS;
x(9) <= '1' when A = "0000000000000000" else '0';
x(10) <= B(0);
end OU;
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.all;
use IEEE.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity CU is
port(
clk,rst:in std_logic;
x:in std_logic_vector(10 downto 1);
y:out std_logic_vector(24 downto 1)
);
end CU;
architecture CU of CU is
subtype TCommand is std_logic_vector(37 downto 0);
type TROM is array (0 to 31) of TCommand;
constant ROM:TROM := (
-- |----------- y --------||x ||-a0||-a1|
"000000000000000000000000 0001 0000111010",--0
"00000000000000000000001100100001000011",--1
"00000000000000000000110000110010000101",--2
"00000001000000000000000000000000000000",--3
"00000000000000000001000000110011011111",--4
"00000000000000000010000000110011011111",--5
"00000000000000001100000000110011101000",--6
"00000000000000010000000000000100101001",--7
"00000000000000100000000000000100101001",--8
"00000000000001000000000001000101001111",--9
"00000000000000000000000000110101101100",--10
"00000000000010000000000000000110101101",--11
"00000000000010000000000000000111001110",--12
"00000000000100000000000000110011101000",--13
"00000000001000000000000000110011101000",--14
"00000000000000000000000001011000010001",--15
"00000000000000000000000001111010011000",--16
"00000000000000000000000001101001010011",--17
"00000000001000000000000001111010011000",--18
"00000000000100000000000001111010011000",--19
"00000000000000000000000010000000010101",--20
"00000000000000000000000010010000010110",--21
"00000000010000000000000000001011110111",--22
"00000000100000000000000000000000000000",--23
"00000000000000000000000010001011011001",--24
"00000000000000000000000010011011000000",--25
"00001100000000001100000010101110011011",--26
"00010000000000000000000000001110011100",--27
"01100000000001000000000001001110111110",--28
"00000000000000000000000010101110011011",--29
"10000000000000000000000000000000000000",--30
"00000010000000000000000000000000000000");
signal RegCom:TCommand;
signal xx:std_logic_vector(10 downto 1);
begin
process (clk,rst) is
variable j:integer:=1;
begin
if rst = '0' then RegCom <= (others => '0');
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
case RegCom(13 downto 10) is
when "0001" => j:=1;
when "0010" => j:=2;
when "0011" => j:=3;
when "0100" => j:=4;
when "0101" => j:=5;
when "0110" => j:=6;
when "0111" => j:=7;
when "1000" => j:=8;
when "1001" => j:=9;
when "1010" => j:=10;
when others =>null;
end case;
if((x(j)='0') or (RegCom(13 downto 10)="0000")) then
RegCom<=ROM(conv_integer(RegCom(9 downto 5))); -- A0
else
RegCom<=ROM(conv_integer(RegCom(4 downto 0))); -- A1
end if;
end if;
end process ;
y <= RegCom (37 downto 14);
end CU;
----------------
--cpu.vhd
----------------
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.all;
use work.all;
entity CPU is
port(
clk,rst:in std_logic;
d1:in std_logic_vector(15 downto 0);
d2:in std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
F:in std_logic;
DBUS:out std_logic_vector(15 downto 0)
);
end CPU;
--}} End of automatically maintained section
architecture cpu of cpu is
component OU
port(
clk,rst:in std_logic;
d1:in std_logic_vector(15 downto 0);
d2:in std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);
f:in std_logic;
y:in std_logic_vector(24 downto 1);
x:out std_logic_vector(10 downto 1);
DBUS:out std_logic_vector(15 downto 0)
);
end component ;
component CU
port (
clk,rst:in std_logic;
x:in std_logic_vector(10 downto 1);
y:out std_logic_vector(24 downto 1)
);
end component ;
signal y: std_logic_vector (24 downto 1);
signal x: std_logic_vector (10 downto 1);
signal nclk: std_logic;
begin
nclk <= not clk;-- after 10 ns;
dd1:OU port map (nclk,rst,d1,d2,f,y,x,DBUS);
dd2:CU port map (clk,rst,x,y);
end cpu;
