
2015 ARKH-P6-Project Management
.pdf
Safety dog
61

RISK MANAGEMENT
OBJECTIVES OF RISK MANAGEMENT
A formalised and structured approach with adequate tools to :
Secure Project objectives
Help decision making
Have a better understanding and control of risks that can prevent you from achieving Project targets for :
Schedule
Budget
Technical specifications / performance / quality
Revenue
62

RISK MANAGEMENT
ORGANISATION
A risk management is not only for large and complex projects. It can be and must be adapted to :
The size and strategic importance of the Project
The level of risk of the Project : complexity, innovations, uncertainties, constraints….
The phase of the Project it is applied to
Minimum :
Light and standard procedures,
Management by a person in charge of a few projects for RM,
Simple Risk tables…
Maximum :
Specific Risk Management Plan,
Full Risk Register, probabilistic cost and schedule models,
Dedicated Risk Assessment Manager…
63

RISK MANAGEMENT
Systematic analysis of the risks
Risk = event that is detrimental to one or several objective(s)
Identification and ranking of the risks
Definition of specific actions linked to the risks:
Mitigation (if possible!)
Monitoring
Empowering experience for the project team members
Enhances the perception of the project stakes
Contributes to the team spirit (management tool)
Is implemented all through the project
Risks evolve over time
Actions are spread out
“Top five” & communication
64
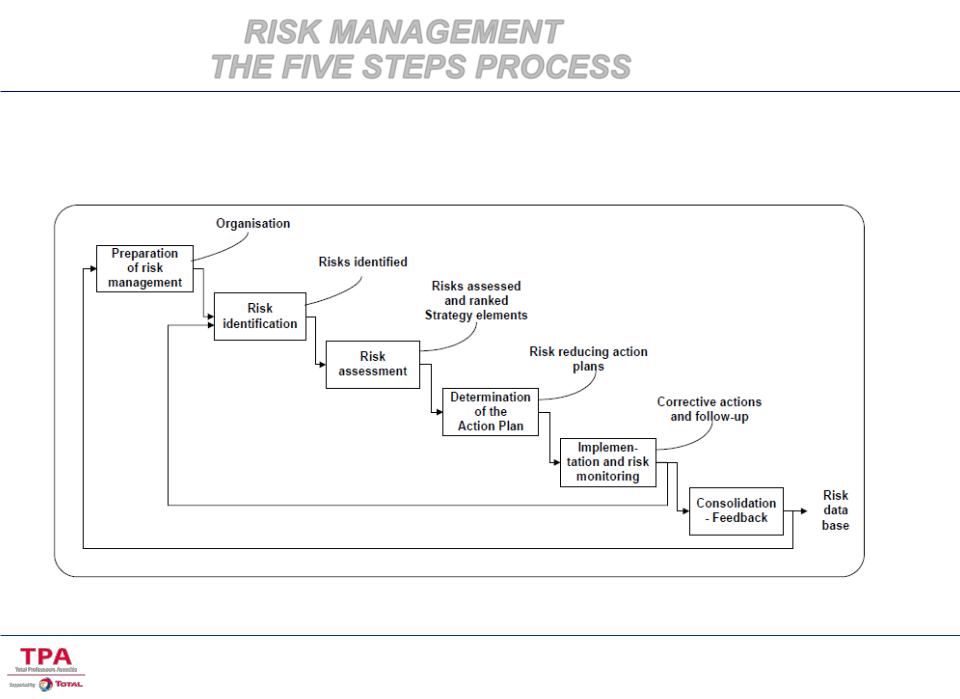
RISK MANAGEMENT THE FIVE STEPS PROCESS
65
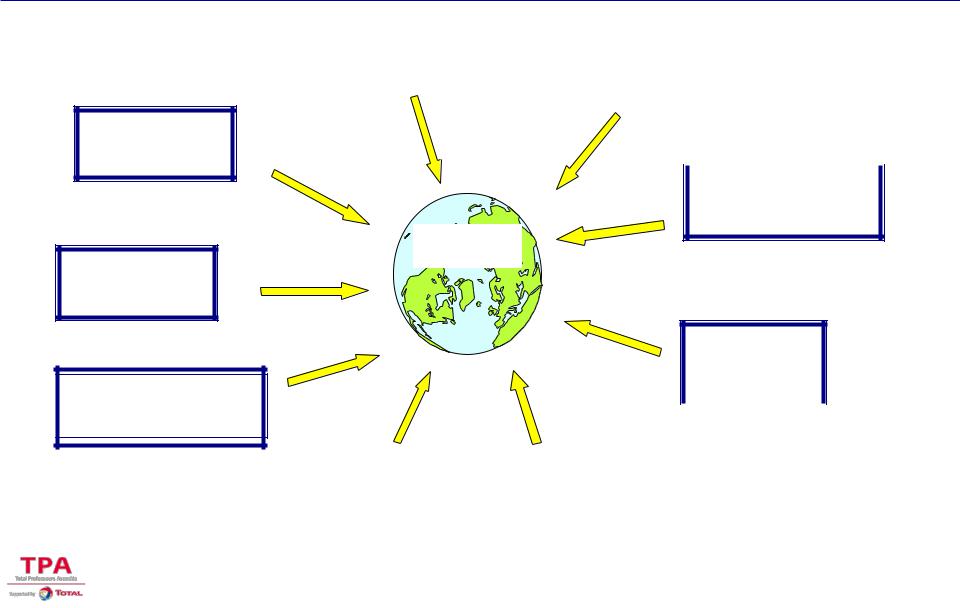
RISK MANAGEMENT –KEY ISSUES
|
|
|
|
|
Exchange |
|
|
|
|
Market & price |
|
|
Rate risks |
|
|
|
|
risks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geological
risks  Kidnapping
Kidnapping  risks
risks
PROJECT
Reserves risks
Political
risks Non-completion 
risks
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating |
|
Environmental |
|
|
|
risks |
|
risks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66

CONSTRUCTION
MANAGEMENT

CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT
WHAT IS CONSTRUCTABILITY ?
“The optimum use of construction knowledge and experience in planning, design, procurement and field operations to achieve overall project objectives”
(CII - Construction Industry Institute Definition)
IN PARTICULAR
Determining more efficient construction methods,for example considering modularization of pre-assembly program
Assigning construction personnel to the engineering office during design
Allowing construction personnel to review design documents periodically
68
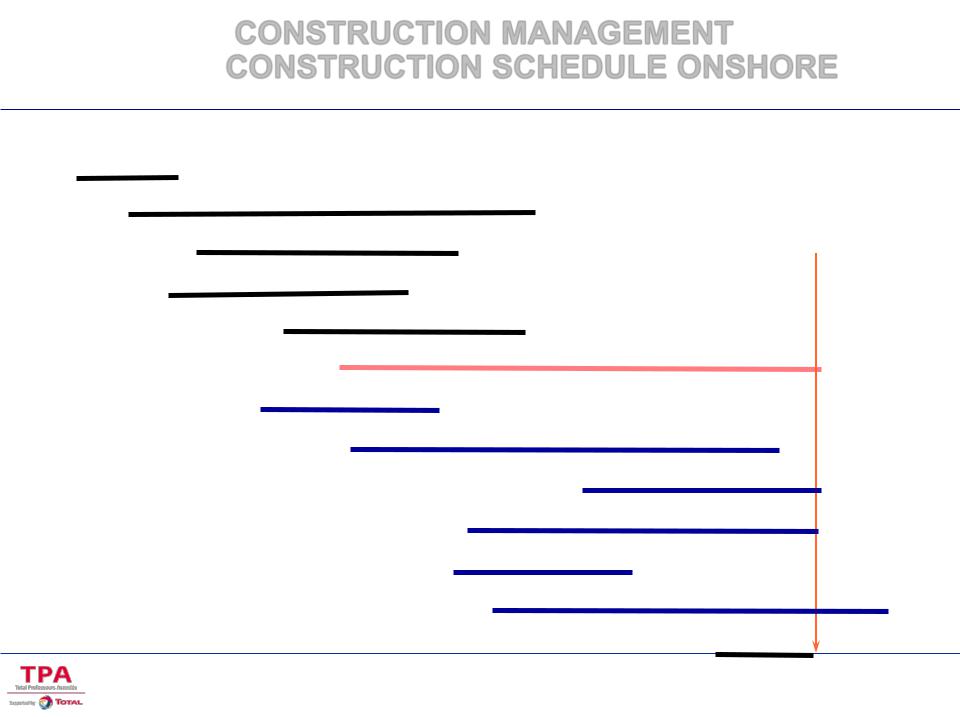
CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT CONSTRUCTION SCHEDULE ONSHORE
Site Preparation
Civil Works, Roads, Railways |
Mechanical |
|
|
Structural Steel |
Completion |
|
|
U/G Piping Installation |
|
Equipment Erection |
|
A/G Piping Erection |
|
U/G Electrical Cables |
Generally on the critical path |
|
|
A/G Electrical Installation |
|
|
Electrical Tracing |
Instrumentation |
|
Fire Proofing
Painting - Insulation
Precommissioning
69

QUALITY MANAGEMENT
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Reflects an established Quality Management “doctrine”
Common understanding of what Quality on a project means
A standardized implementation of company principles
A better guarantee to get what is expected
A COMMON SENSE doctrine!
The principles must be practical and applicable
The objective is not to work “for art’s sake”
The objective is not to generate heaps of documents
A TRACEABLE common sense!
Some rules need to be followed
« Who (has done) does what, why and when? »
70 |
70 |
