
- •I.В. Знаменська
- •Contents
- •Передмова
- •Hippocratic oath
- •Unit 1 lesson 1
- •Vocabulary
- •Phonetics
- •Grammar:
- •(Interrogative Form)
- •(Negative Form)
- •To have
- •Pronoun
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •I am a medical student
- •Personal Information Sheet
- •1. Tell your fellow-students about yourself.
- •2. Describe your family to your new friend.
- •3. Show a friend your family album and answer all his/her questions.
- •Ex. 38. You want to get some information about your patient. Ask him/her questions using the expressions of 36thexercise. Overview
- •Lesson 2
- •Vocabulary
- •Phonetics
- •Grammar: word order in a statement
- •Article
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ukrainian medical stomatological academy
- •Medical university
- •Overview
- •Lesson 3
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Vowels (голосні)
- •Word-building
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Medical education in ukraine
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •(Interrogative Form)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Medical education in the usa
- •Medical education in the united kingdom
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Forms of the verb
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Profession of the physician
- •How often should I consult my physician
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Grammar:
- •Impersonal sentences
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ex. 9. What famous physicians of the present do you know? What field of medicine do they work in?
- •Prominent scientists and physicians of ukraine
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Grammar:
- •Simple tenses (Affirmative Form, Active Voice)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Public health service in ukraine
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •National health service in the united kingdom
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Simple tenses (Interrogative Form, Active Voice) General Questions
- •Special Questions
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Polyclinic
- •Overview
- •Medical examination
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Reading and developing speaking skills Ex. 7. Read vocabulary and memorize new words. Ex. 8. Compose 5-6 sentences using the words of the vocabulary
- •At the therapeutist's
- •Overview
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Open conditionals
- •Numeral
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Hospital
- •Ex. 19. Translate the following sentences into English:
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •At the physician's
- •1. In what order you might ask these questions; 2. In what form you might ask them:
- •Overview
- •Lesson 13
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Grammar:
- •Modal verbs
- •Equivalents of the modal verbs
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Chemist’s shop
- •Your home medicine chest
- •Overview
- •I. Insert the missing words:
- •II. Finish the following sentences:
- •III. Choose the proper term given below to the following definitions:
- •IV. Read and translate one of the following texts:
- •Galen (philosopher, physician, discoverer of blood and the cranial nerves)
- •World health organization
- •V. Speak on the following topics:
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Simple tenses (Passive Voice, Affirmative Form)
- •Passive voice:
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Body regions
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Simple tenses (Passive Voice, Interrogative Form)
- •General Questions
- •Special Questions
- •Reading and developing speaking skills Ex. 8. Insert the missing letters and translate the following words:
- •Ex. 12. Read the following text: trunk
- •Body cavities
- •Directional terms for humans
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Lesson 18
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Perfect tenses (Active Voice, Affirmative Form)
- •Modal verbs: should and would
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ex. 18. Do you agree, disagree or partially agree with the statements below:
- •Cell division
- •Ex. 25. Answer the following questions:
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading
- •Reading and developing speaking
- •Tissues
- •Classification of Epithelium
- •Tissues and organs
- •Functions and Location of Tissues.
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking
- •Organ systems
- •Ex. 16. Translate the following sentences into English:
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading mute letters (“німі” літери)
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Participle I (v4)
- •Continuous tenses (Active Voice, Affirmative Form)
- •Reading and developing skills
- •Skeleton
- •Ex. 26. Read the following words and try to memorize them:
- •Bone's structure
- •Overview
- •Lesson 22
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Fractures, dislocations, sprains, and strains
- •Fractures
- •Dislocations
- •Sprains
- •Strains
- •The signs of fractures, dislocations, sprains, and strains
- •Ex. 11. What types of dislocations and fractures do you know? Can you explain the meaning of the following terms:
- •Types of fractures
- •First aid
- •At the traumatologist’s
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading mute letters (“німі” літери)
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Continuous tenses (Active Voice, Interrogative Form)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Muscles
- •Ex. 23. Make up a detailed plan of the text "Muscles".
- •Ex. 26. Read the following text and answer the question: Is the body-building useful for modern people? body-building
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and developing speaking skills Ex. 1. Insert the missing letters:
- •Emergency care of wounds
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Rules of reading mute letters (“німі” літери)
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Continuous tenses (Passive Voice, Affirmative Form)
- •Indefinite pronouns and adverbs
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Digestive system
- •Portions of the digestive system
- •Gallbladder
- •Pancreas
- •Large intestine
- •The alimentary tract
- •At the gastroenterologist’s
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Stomach
- •Stomach functions
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Perfect tenses (Passive Voice, Affirmative Form)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Overview
- •Lesson 28
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Perfect tenses (Passive Voice, Interrogative Form)
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Ex. 8. Translate the following words and word-combinations into Ukrainian:
- •Ex. 14. Answer the following questions:
- •Formed elements of the blood
- •Platelets
- •Leukocytes
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Perfect tenses
- •(Passive Voice)
- •(Revision)
- •Object clauses
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Blood groups
- •Ex. 19. Find the corresponding Ukrainian equivalents for the English terms:
- •Ex. 20. Pronounce and memorize the words to the theme studied:
- •Ex. 21. Read the following text: blood transfusion
- •Summary
- •І. Головна тема чи проблема:
- •Іі. Мета вивчення:
- •Ііі. Зазначення основних положень:
- •IV. Применение на практике
- •V. Висновки та результати:
- •Overview
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Attributive clauses
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Suggestions for useful phrases:
- •Ex. 27. Translate the following interrogative sentences into English:
- •Heart chambers
- •Vessels
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar:
- •Adverbial clauses
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •Blood vessels
- •General features of blood vessel structure
- •Lesson 32
- •Vocabulary
- •Word-building
- •Grammar: subordinate clauses
- •Reading and developing speaking skills
- •The cardiac cycle
- •At the cardiologist’s
- •Overview
- •Lesson 33
- •II. Insert the correct form of the verb:
- •III. Translate the following sentences:
- •IV. Read and translate one of the following texts: Text a disorders of the heart and blood vessels
- •Text b atherosclerosis
- •Text c leukemia
- •Text d digestive system
- •Peptic ulcer
- •Text f gastritis
- •V. Speak on the following topics:
- •Appendix 1
- •Irregular verbs
- •Appendix 2 suffixes and term-elements
- •Term elements of greek and latin origin greek, latin, english and ukrainian equivalents
- •Короткий довідник з правил словотворення
- •Найуживаніші суфікси англійської мови:
- •Основні префікси:
- •Practical grammar guide
- •(Короткий граматичний довідник)
- •Іменник
- •(Cases)
- •Артикль (article)
- •Займенники (pronouns)
- •Прикметник (adjective)
- •Найвищий ступінь порівняння прикметників (Superlative Degree)
- •Порядок слів у реченні.
- •Побудова розповідних і питальних речень
- •Способи визначення присудка в англійському реченні
- •Неозначено-особові речення
- •Безособові речення.
- •Форми дієслова forms of the verb
- •Часи групи simple (indefinite) present simple
- •Past simple
- •Future simple
- •Simple tenses
- •Часи групи continuous
- •Present continuous
- •Past continuous
- •Future continuous
- •Continuous tenses
- •Perfect tenses
- •Present perfect
- •Past perfect
- •Future perfect
- •Perfect tenses
- •Стан дієслова
- •Passive voice
- •Зведена таблиця часів стверджувальної форми
- •Зведена таблиця питальної форми
- •Interrogative form
- •Дієслова to be та to have
- •Ознаки функціональної відмінності дієслова to be
- •Модальні дієслова (modal verbs)
- •Модальне дієслово can
- •Модальне дієслово could
- •Модальне дієслово may
- •Модальне дієслово must
- •Ознаки розпізнавання граматичних форм, утворених за допомогою допоміжних дієслів should I would
- •Підрядні додаткові та означальні речення (object clauses)
- •Виділення членів речення за допомогою підсилювальної конструкції it is (was, will be) ... That (who, which)
- •Умовний спосіб
- •(Infinitive)
- •Об’єктний інфінітивний комплекс (Objective Infinitive Construction)
- •Дієприкметник
- •Об’єктний дієприкметниковий комплекс (Objective Participle Construction)
- •The Objective Participle Construction перекладається підрядним реченням зі сполучником “як”: I saw them walking along the street. – я бачив, як вони йшли по вулиці. Герундій (gerund)
- •Форми герундія
- •Герундіальний комплекс (зворот) (Gerund Construction)
- •Узгодження часів у підрядному додатковому реченні
- •Vocabulary список використаної літератури
- •І.В. Знаменська о.О. Пісоцька в.Г. Костенко
Ex. 26. Read the following words and try to memorize them:
Epiphysis [e'pIfIsIs] епіфіз; epiphyseal line [epI'fIzIql] епіфізарна лінія; cartilage ['ka:tIlIG] хрящ; compact bone ['kOmpxkt 'boun] компактна кісткова тканина; cancellous bone ['kxnsqlqs] сітчаста кістка, губчаста кісткова речовина; spongy bone ['spAnGI] губчаста кісткова речовина; matrix ['meItrIks] матрикс, основа, міжклітинний матеріал; сavity ['kxvItI] порожнина; rigid ['rIGId] жорсткий, негнучкий, твердий; medullary [me'dAlqrI] медулярний, мозковий; серцевинний; maintain [meIn'teIn] підтримувати, утримувати, зберігати; support [sq'pO:t] підтримка; sinus ['saInqs] пазуха; fill with [fIl] наповнювати(ся); band [bxnd] зв'язка; approximately [q'prOksImItlI] близько, приблизно; marrow ['mxrqu] кістковий мозок; broad [brO:d] широкий; periosteum ["perI'OstIqm] окістя, надкісниця; fit [fIt] підходити, відповідати; dense [dens] щільний, густий; diaphysis [daI'xfIsIs] діафіз, середня частина трубчастої кістки.
Ex. 27. Read the following text:
Bone's structure
The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages, tendons, and ligaments. Because bone is very rigid, it is well adapted to help maintain the shape of the body and protect internal organs. Cartilages, which are somewhat rigid but more flexible than bones, also provide support. Tendons and ligaments are strong bands of fibrous connective tissue. Tendons attach muscles to the bones, and ligaments attach bones to bones.
Individual bones can be classified according to their shape as long, short, flat, or irregular. Most of the bones of the upper and lower limbs are long bones. These bones are very strong. They are broad at the ends where they join with other bones, and have large surface areas for muscle attachment. Short bones are approximately as broad as they long. They are nearly cube shaped or round. They are in the wrist and ankle. Flat bones have a relatively thin, flattened shape. The examples of flat bones are some skull bones, ribs, pelvic bones, and the breastbone (sternum). Irregular bones are ones such as the vertebrae and facial bones with shapes that do not fit into three categories.
Each long bone consists of three major components: the diaphysis; an epiphysis; and the epiphyseal line (or epiphyseal plate in each growing long bone). The diaphysis is long middle region of a long bone composed of compact bone, which is bone matrix. Each end of a long bone is called an epiphysis. The epiphyses consisting of cancellous bone (sometimes called spongy bone), has many small spaces or cavities within the bone matrix. The outer surface of the epiphyses consists of a layer of compact bone. In addition to the small spaces within cancellous bone and compact bone, some bones contain large cavities. The diaphyses of long bones have a large medullary cavity (some of the skull bones have spaces called sinuses). The medullary cavity and the cavities of the cancellous bone are filled with marrow. Medullary cavity contains yellow bone marrow and spaces in cancellous bone contain red bone marrow. Yellow bone marrow is mostly composed of adipose tissue. Red bone marrow is the site of blood formation. In general, yellow marrow is associated with the long bones of the limbs, and red marrow is associated with the rest of the skeleton. The outer surface of bones consists of a periosteum. The periosteum is a strong, fibrous, vascular membrane that covers the surface of a long bone, except at the ends of the epiphyses. The inner layer consists mostly of a single layer of osteoblasts with a few osteoclasts. Osteoblasts are bone producing cells, and osteoclasts are cells breaking down bone.
Flat bones usually have no diaphyses or epiphyses. They contain an interior framework of cancellous bone sandwiched between two layers of compact bone. Short and irregular bones have a composition similar to the epiphyses of long bones. They have compact bone surfaces surrounding a cancellous bone center with small spaces that usually filled with marrow. Short and irregular bones have no diaphyses. However, certain regions of these bones (e.g., the processes of irregular bones) have epiphyseal growth plates and therefore have small epiphyses.
Ex. 28. Answer the following questions:
1. What does the skeletal system consist of? 2. What is the major function of the bone? 3. What does the cartilage provide? 4. What are ligaments and tendons? 5. What are their functions? 6. What types of bones do you know? 7. What components does every long bone consist of? 8. What is diaphysis composed of? 9. What does the epiphysis consist of? 10. What is compact bone? 11. What is osteoblast? 12. What is osteoclast? 13. What do the flat bones contain? 14. What are short and irregular bones composed of?
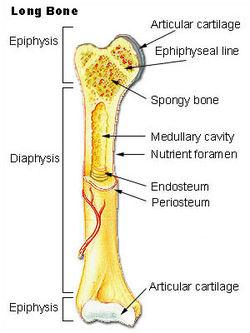
Structure of Bone
Ex. 29. Match the following terms with their definitions:
|
1. Cartilage |
1. noncellular substance surrounding the cells of connective tissue. |
|
2. Ligament |
2. dense plate of bone in a bone that is no longer growing, indicating the former site of the epiphyseal plate. |
|
3. Tendon |
3. similar molecules binding to the same carrier molecule or receptor site. |
|
4. Compact bone |
4. band of dense connective tissue connecting a muscle to a bone or other structure. |
|
5. Epiphyseal line |
5. portion of a bone developed from a secondary ossification center and separated from the remainder of the bone by the epiphyseal plate. |
|
6. Epiphysis |
6. band of dense connective tissue connecting two or more bones, cartilages, or other structures. |
|
7. Matrix |
7. firm, smooth, nonvascular connective tissue. |
