
- •1.Describe the bureaucratic form of organization, and discuss its advantages and disadvantages.
- •2. Explain the major ways in which organizations are divided into departments.
- •3.Describe three modifications of the bureaucratic structure: the matrix organization; flat structures; and the horizontal structure.
- •4.Specify how delegation, empowerment, and decentralization spread authority in an organization.
- •5.Identify major aspects of organizational culture, including its management and control.
- •6.Describe key aspects of managing change, including gaining support for change.
- •7.Describe the process of management, including the functions of management.
- •8.Identify the basic managerial skills and explain how they can be developed.
- •9.Identify the major developments in the evolution of management thought.
- •Administrative management
- •3.Bureaucratic management
- •10.Describe the steps in the communication process.
- •11.Recognise the major types of nonverbal communication in the workplace.
- •12.Explain and illustrate the difference between formal and informal communication channels.
- •13. Identify major communication barriers in organizations.
- •14.Describe how to conduct more effective meetings.
- •15.Develop tactics for overcoming communication barriers.
- •16.Describe the stages of group development.
- •17.Refer to the potential contributions and problems of teams and groups.
- •18.Describe the positive and negative aspects of conflicts and how team leaders and managers can resolve conflict.
- •19.Differentiate between leadership and management.
- •20.Describe how leaders are able to influence and empower members.
- •21.Explain what the term manager means, and identify different types of managers.
- •22.Describe the nature of business strategy.
- •23.Explain how business strategy is developed, including swot analysis.
- •24. Describe how to use Gantt charts and pert planning techniques.
- •25. Describe how to use break-even analysis.
- •26. Explicate decision trees or problem solving and decision making.
- •Decision-making process
- •27. Set out how to identify problems using a Pareto diagram.
- •28. Explain the relationship among motivation, performance, and commitment.
- •Improved management control
- •29. Explain how goal setting is used to motivate people.
- •30. Present an overview of major theories of need satisfaction in explaining motivation.
- •31.Identify major assumptions of Theory X.
- •32.Identify major assumptions of Theory y.
- •33.Dwell upon Contingency theory
- •34. Set out Scientific Management Theory.
- •35.Set out Administrative Management Theory.
- •36.Recite Behavioral Management Theory.
- •37.Propone the Nature of Motivation.
- •38. Set forth Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
- •39. State Herzberg's Motivator-Hygiene Theory
- •40. Dwell on Sources of Managerial Power.
- •Legitimate Power
- •Expert power
- •Referent Power
- •Coercive Power
- •Reward Power
- •41.According to the given information create a network and find out critical path.
- •42.According to the given information create a network and find out critical path.
- •43.The company "Garden-plot" produces garden gnomes and sells them at ₤ 60 per unit. The costs of the company are:
- •44.The company "Master Bread" produces pies and sells them at 4000 tenge per unit. The costs of the company are:
- •45.The company "Garden-plot" produces garden gnomes and sells them at ₤ 60 per unit. The costs of the company are:
- •46.The company "Garden-plot" produces garden gnomes and sells them at ₤ 60 per unit. The costs of the company are:
- •47. According to the given information create a Gantt chart.
- •48. According to the given information create a Gantt chart.
- •49. According to the given information create a network.
- •50.According to the given information create a network and find out the Critical path.
- •51.Draw an Ishikawa diagram to improve performance of your Dean Office. Take into account primary and secondary causes related with
- •53.Mini-case the go-slow culture at motorola
- •1. What about the Motorola culture does Zander want to change?
- •2. Speculate on what Zander might do to change the Motorola culture.
- •54. Describe the bureaucratic form of organization, and discuss its advantages and disadvantages.
- •55. Explain the major ways in which organizations are divided into departments.
- •56. There are two measurements. It has been determined the age and income of a number of people, as shown in the Table 1. What can be said about the relationship between the values of the X and y?
- •57. There are two measurements. It has been determined the age and income of a number of people, as shown in the Table 1. What can be said about the relationship between the values of the X and y?
- •58. Consider the project defined by the dependencies in Table. Create a network and find out critical path.
- •59. Consider the project defined by the dependencies in Table. Create a network and find out critical path.
- •60. The company "Snowman" produces New Year's trees and sells them at kzt 4500 per unit. The costs of the company are:
Decision-making process
Define and clarify the issue - does it warrant action? If so, now? Is the matter urgent, important or both. See the Pareto Principle.
Gather all the facts and understand their causes.
Think about or brainstorm possible options and solutions. (See brainstorming process)
Consider and compare the 'pros and cons' of each option - consult others if necessary or useful - and for bigger complex decisions where there are several options, create a template which enables measurements according to different strategic factors (see SWOT, PEST, Porter).
Select the best option - avoid vagueness and weak compromises in trying to please everyone.
Explain your decision to those involved and affected, and follow up to ensure proper and effective implementation.
27. Set out how to identify problems using a Pareto diagram.
When to Use a Pareto Chart
When analyzing data about the frequency of problems or causes in a process.
When there are many problems or causes and you want to focus on the most significant.
When analyzing broad causes by looking at their specific components.
When communicating with others about your data.
Pareto Chart Procedure
Decide what categories you will use to group items.
Decide what measurement is appropriate. Common measurements are frequency, quantity, cost and time.
Decide what period of time the Pareto chart will cover: One work cycle? One full day? A week?
Collect the data, recording the category each time. (Or assemble data that already exist.)
Subtotal the measurements for each category.
Determine the appropriate scale for the measurements you have collected. The maximum value will be the largest subtotal from step 5. (If you will do optional steps 8 and 9 below, the maximum value will be the sum of all subtotals from step 5.) Mark the scale on the left side of the chart.
Construct and label bars for each category. Place the tallest at the far left, then the next tallest to its right and so on. If there are many categories with small measurements, they can be grouped as “other.”
Steps 8 and 9 are optional but are useful for analysis and communication.
Calculate the percentage for each category: the subtotal for that category divided by the total for all categories. Draw a right vertical axis and label it with percentages. Be sure the two scales match: For example, the left measurement that corresponds to one-half should be exactly opposite 50% on the right scale.
Calculate and draw cumulative sums: Add the subtotals for the first and second categories, and place a dot above the second bar indicating that sum. To that sum add the subtotal for the third category, and place a dot above the third bar for that new sum. Continue the process for all the bars. Connect the dots, starting at the top of the first bar. The last dot should reach 100 percent on the right scale.
Pareto Chart Examples
Example #1 shows how many customer complaints were received in each of five categories.
Example #2 takes the largest category, “documents,” from Example #1, breaks it down into six categories of document-related complaints, and shows cumulative values.
If all complaints cause equal distress to the customer, working on eliminating document-related complaints would have the most impact, and of those, working on quality certificates should be most fruitful.
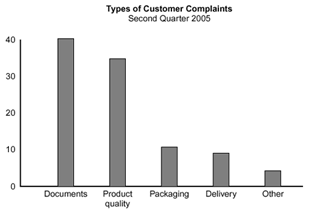 Example
#1
Example
#1

